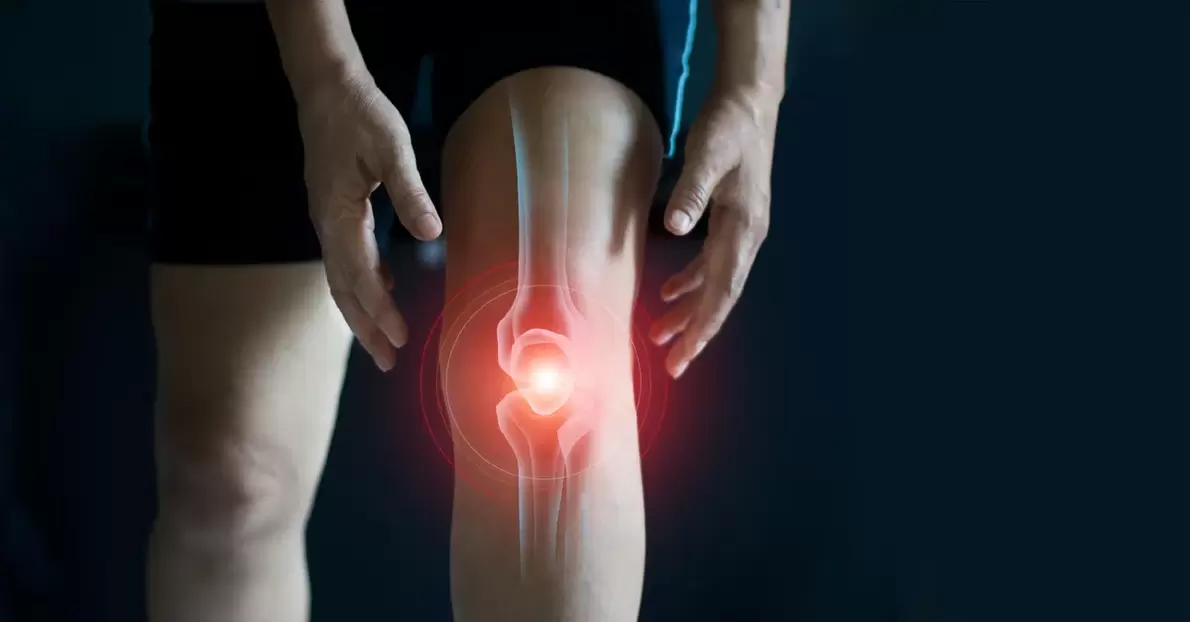
The knee joint is one of the largest joints in the human body. Because it takes almost all the weight of our body, it is subjected to a huge load. The knee joint is often injured.
The presence of knee pain can be a sign of a serious pathology. Pain in the knee joint not only limits movement and causes discomfort, but can also cause disability.
How is knee pain?
Knee pain is a common complaint and can occur in people of all ages. Pain in the knee joint itself is not only the result of an injury, but can also be a sign of a serious disease (osteoarthritis, gout).
There are two types of pain: acute and chronic. Acute knee pain most often occurs as a result of an injury or is a symptom of an acute inflammatory process.
Chronic knee pain is characterized by a gradual increase in pain. The main cause of chronic pain is the development of degenerative-dystrophic changes or chronic inflammatory process in the tissues of the joint. The most characteristic for a chronic process is the presence of aching pain in the knee joint.
By its nature, pain in the knee joint can be bending, painful and can be accompanied by a number of other manifestations:
- Swelling and redness in the joint area;
- joint deformation;
- limitation of movements in the joint;
- The presence of a crisis in the joint during movement.
Causes of knee pain
Knee pain can be a result of aging and wear and tear on the components of the knee joint. The most common cause of acute pain in the knee is trauma and damage to the joint. The most common knee injuries are:
- Fractures and bruises, which most often occur during a fall and are accompanied by sharp pain;
- torn ligaments or tendons;
- meniscus tear;
- Dislocation of both the knee joint itself and the patella.
Against the background of injury and damage to the knee joint, diseases such as bursitis and tendonitis can develop.
Other causes of pain in the knee joint include the presence of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the tissues of the joint, as well as inflammatory processes:
- Bursitis. Bursitis is an inflammation of the joint bag, accompanied not only by pain, but also by swelling.
- Tendinitis. Tendonitis is inflammation of one or more tendons. This inflammation can occur when the tendons of the patella are damaged. Most often, they are found in people who are professionally engaged in running, jumping, skiing, as well as cyclists.
- Arthritis is inflammation of a joint. The most common is osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease in which all components of the joint are affected, primarily cartilage, ligaments, capsules and muscles. Joint inflammation can also be infectious (septic arthritis) and autoimmune (rheumatoid arthritis).
Less common causes of knee pain include cysts and tumors that compress nearby tissues and cause pain in the knee joint.
A number of factors can increase your risk of knee pain:
- Excess weight. Being overweight or obese puts more stress on the knee joints, which increases the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Having knee joint injuries in the past.
- certain sports. Some sports put a lot of stress on the knee joint, which increases the risk of chronic injury.
- The presence of diseases such as osteomyelitis and osteoporosis, which cause brittle bones, thereby increasing the risk of fractures.
Knee pain when walking
Pain in the knee joint that increases with movement is most often a sign of degenerative-dystrophic diseases (osteoarthritis). Pain is caused by contact during movement of articular surfaces that lack cartilage tissue to a certain extent.
Knee pain during extension and bending
Pain in the knee during extension and bending indicates an inflammatory process in the tendon-ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint, and also occurs with inflammation of the articular bag (bursitis). Inflammation in the tendon-ligamentous apparatus of the knee joint can occur when the tendon of the patella is damaged. Often, this pathology occurs in people who practice sports.
The second cause of pain when bending and extending the knee joint is degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cartilage tissue of the joint (osteoarthritis).
Knee pain at rest
Aching pain in the knee at rest, especially at night, is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis. Other causes include sprains, damage to the meniscus, cartilage, inflammation of the tendons (tendinitis), and inflammation of the periarticular sac (bursitis).
Knee pain at night increases with age and is often seen in people who are overweight.
What not to do with pain syndrome
First of all, you should not self-medicate, but it is better to immediately seek help from a specialist. In any case, if there is a dislocation, do not try to fix the joint yourself.
Avoid sudden movements, do not create a large load on the joint - this can only increase the pain.
Diagnostics
If you have pain in the knee joint, you should consult an orthopedic doctor. First of all, the specialist asks the patient, collects complaints and conducts a thorough examination. To rule out mutual pathologies, the doctor can schedule consultations with other specialists, for example, a neurologist.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include x-ray examination, magnetic resonance or computer tomography (MRI / CT) and ultrasound of knee joints.
Laboratory research methods are general and biochemical blood tests.
Treatment of knee pain
Depending on the nature of the lesion, the specialist prescribes a special treatment plan. Often, the treatment of knee pain is complex and includes drug and non-drug treatment.
Drug therapy includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and analgesics. These drugs reduce inflammation and pain in the joint. Slow-acting drugs or the group of chondroprotectors are also prescribed in 3-6 month courses, which help to reduce inflammation, joint pain, and also slow down the destruction of cartilage, for example, these drugs include combined drugs with glucosamine substances. and chondroitin sulfate.
Non-drug therapy is based on physiotherapeutic methods: UHF, massage, physiotherapy exercises, mud therapy, magnetic therapy, etc. It is also recommended to wear special orthopedic insoles or shoes selected individually by the doctor.
If conservative methods are ineffective, the treatment of knee pain requires a more serious approach: the doctor may recommend various surgical methods of treatment.
































